https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-021-09169-7
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
On the scalar  form factor beyond the elastic region
form factor beyond the elastic region
1
Forschungszentrum Jülich, Institute for Advanced Simulation, Institut für Kernphysik, and Jülich Center for Hadron Physics, 52425, Jülich, Germany
2
Albert Einstein Center for Fundamental Physics, Institute for Theoretical Physics, University of Bern, Sidlerstrasse 5, 3012, Bern, Switzerland
3
Helmholtz-Institut für Strahlen- und Kernphysik and Bethe Center for Theoretical Physics, Universität Bonn, 53115, Bonn, Germany
Received:
4
March
2021
Accepted:
19
April
2021
Published online:
14
May
2021
Pion–kaon (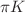 ) pairs occur frequently as final states in heavy-particle decays. A consistent treatment of
) pairs occur frequently as final states in heavy-particle decays. A consistent treatment of 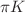 scattering and production amplitudes over a wide energy range is therefore mandatory for multiple applications: in Standard Model tests; to describe crossed channels in the quest for exotic hadronic states; and for an improved spectroscopy of excited kaon resonances. In the elastic region, the phase shifts of
scattering and production amplitudes over a wide energy range is therefore mandatory for multiple applications: in Standard Model tests; to describe crossed channels in the quest for exotic hadronic states; and for an improved spectroscopy of excited kaon resonances. In the elastic region, the phase shifts of 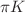 scattering in a given partial wave are related to the phases of the respective
scattering in a given partial wave are related to the phases of the respective 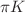 form factors by Watson’s theorem. Going beyond that, we here construct a representation of the scalar
form factors by Watson’s theorem. Going beyond that, we here construct a representation of the scalar 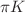 form factor that includes inelastic effects via resonance exchange, while fulfilling all constraints from
form factor that includes inelastic effects via resonance exchange, while fulfilling all constraints from 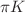 scattering and maintaining the correct analytic structure. As a first application, we consider the decay
scattering and maintaining the correct analytic structure. As a first application, we consider the decay 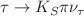 , in particular, we study to which extent the S-wave
, in particular, we study to which extent the S-wave 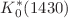 and the P-wave
and the P-wave 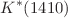 resonances can be differentiated and provide an improved estimate of the CP asymmetry produced by a tensor operator. Finally, we extract the pole parameters of the
resonances can be differentiated and provide an improved estimate of the CP asymmetry produced by a tensor operator. Finally, we extract the pole parameters of the 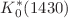 and
and 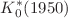 resonances via Padé approximants,
resonances via Padé approximants, ![$$\sqrt{s_{K_0^*(1430)}}=[1408(48)-i\, 180(48)]\,\text {MeV}$$](/articles/epjc/abs/2021/05/10052_2021_Article_9169/10052_2021_Article_9169_tex_eq14.png) and
and ![$$\sqrt{s_{K_0^*(1950)}}=[1863(12)-i\,136(20)]\,\text {MeV}$$](/articles/epjc/abs/2021/05/10052_2021_Article_9169/10052_2021_Article_9169_tex_eq15.png) , as well as the pole residues. A generalization of the method also allows us to formally define a branching fraction for
, as well as the pole residues. A generalization of the method also allows us to formally define a branching fraction for 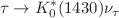 in terms of the corresponding residue, leading to the upper limit
in terms of the corresponding residue, leading to the upper limit  .
.
© The Author(s) 2021
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3




