https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-020-08611-6
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Effects of longitudinal short-distance constraints on the hadronic light-by-light contribution to the muon 
Faculty of Physics, University of Vienna, Boltzmanngasse 5, 1090, Vienna, Austria
b
massimiliano.procura@univie.ac.at
Received:
10
June
2020
Accepted:
29
October
2020
Published online:
2
December
2020
We present a model-independent method to estimate the effects of short-distance constraints (SDCs) on the hadronic light-by-light contribution to the muon anomalous magnetic moment  . The relevant loop integral is evaluated using multi-parameter families of interpolation functions, which satisfy by construction all constraints derived from general principles and smoothly connect the low-energy region with those where either two or all three independent photon virtualities become large. In agreement with other recent model-based analyses, we find that the SDCs and thus the infinite towers of heavy intermediate states that are responsible for saturating them have a rather small effect on
. The relevant loop integral is evaluated using multi-parameter families of interpolation functions, which satisfy by construction all constraints derived from general principles and smoothly connect the low-energy region with those where either two or all three independent photon virtualities become large. In agreement with other recent model-based analyses, we find that the SDCs and thus the infinite towers of heavy intermediate states that are responsible for saturating them have a rather small effect on  . Taking as input the known ground-state pseudoscalar pole contributions, we obtain that the longitudinal SDCs increase
. Taking as input the known ground-state pseudoscalar pole contributions, we obtain that the longitudinal SDCs increase  by
by  , where the isovector channel is responsible for
, where the isovector channel is responsible for 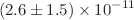 . More precise estimates can be obtained with our method as soon as further accurate, model-independent information about important low-energy contributions from hadronic states with masses up to 1–2 GeV become available.
. More precise estimates can be obtained with our method as soon as further accurate, model-independent information about important low-energy contributions from hadronic states with masses up to 1–2 GeV become available.
© The Author(s) 2020
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3




