https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-020-8312-0
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Relativistic approach to the kinematics of large-scale peculiar motions
1
Section of Astrophysics, Astronomy and Mechanics, Department of Physics, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, 54124, Greece
2
Sorbonne Universités, UPMC Univ Paris 06, CNRS, Institut d’Astrophysique de Paris (IAP), 98bis Boulevard Arago, Paris, 75014, France
3
DAMTP, Centre for Mathematical Sciences, University of Cambridge, Wilberforce Road, Cambridge, CB3 0WA, UK
4
Present address: Department of Physics, The Oscar Klein Centre, Albanova University Center, Stockholm University, 106 91, Stockholm, Sweden
* e-mail: tsagas@astro.auth.gr
Received:
28
May
2020
Accepted:
31
July
2020
Published online:
19
August
2020
We consider the linear kinematics of large-scale peculiar motions in a perturbed Friedmann universe. In so doing, we take the viewpoint of the “real” observers that move along with the peculiar flow, relative to the smooth Hubble expansion. Using relativistic cosmological perturbation theory, we study the linear evolution of the peculiar velocity field, as well as the expansion/contraction, the shear and the rotation of the bulk motion. Our solutions show growth rates considerably stronger than those of the earlier treatments, which were mostly Newtonian. On scales near and beyond the Hubble radius, namely at the long-wavelength limit, peculiar velocities are found to grow as 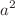 , in terms of the scale factor, instead of the Newtonian
, in terms of the scale factor, instead of the Newtonian 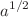 -law. We attribute this to the fact that, in general relativity, the energy flux, triggered here by the peculiar motion of the matter, also contributes to the local gravitational field. In a sense, the bulk flow gravitates, an effect that has been bypassed in related relativistic studies. These stronger growth-rates imply faster peculiar velocities at horizon crossing and higher residual values for the peculiar-velocity field. Alternatively, one could say that our study favours bulk peculiar flows larger and faster than anticipated.
-law. We attribute this to the fact that, in general relativity, the energy flux, triggered here by the peculiar motion of the matter, also contributes to the local gravitational field. In a sense, the bulk flow gravitates, an effect that has been bypassed in related relativistic studies. These stronger growth-rates imply faster peculiar velocities at horizon crossing and higher residual values for the peculiar-velocity field. Alternatively, one could say that our study favours bulk peculiar flows larger and faster than anticipated.
© The Author(s), 2020




