https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-019-7382-3
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Global analysis of dark matter simplified models with leptophobic spin-one mediators using MasterCode
1
Paul Scherrer Institut, 5232, Villigen, Switzerland
2
DESY, Notkestrasse 85, 22607, Hamburg, Germany
3
High Energy Physics Group, Blackett Laboratory, Imperial College, Prince Consort Road, London, SW7 2AZ, UK
4
Institute of Theoretical Physics, Faculty of Physics, University of Warsaw, ul. Pasteura 5, 02-093, Warsaw, Poland
5
Physikalisches Institut, Ruprecht-Karls-Universität, 69120, Heidelberg, Germany
6
Experimental Physics Department, CERN, 1211, Geneva 23, Switzerland
7
Antwerp University, 2610, Wilrijk, Belgium
8
ARC Centre of Excellence for Particle Physics at the Terascale, School of Physics, University of Melbourne, Melbourne, 3010, Australia
9
Theoretical Particle Physics and Cosmology Group, Department of Physics, King’s College London, London, WC2R 2LS, UK
10
National Institute of Chemical Physics and Biophysics, Rävala 10, 10143, Tallinn, Estonia
11
Theoretical Physics Department, CERN, 1211, Geneva 23, Switzerland
12
H.H. Wills Physics Laboratory, University of Bristol, Tyndall Avenue, Bristol, BS8 1TL, UK
13
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, 60208-3112, USA
14
Instituto de Física Teórica UAM-CSIC, C/Nicolas Cabrera 13-15, 28049, Madrid, Spain
15
Campus of International Excellence UAM+CSIC, Cantoblanco, 28049, Madrid, Spain
16
Instituto de Física de Cantabria (CSIC-UC), Avda. de Los Castros s/n, 39005, Santander, Spain
17
Instituto Galego de Física de Altas Enerxías, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Spain
18
William I. Fine Theoretical Physics Institute, School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, 55455, USA
* e-mail: kazuki.sakurai.1225@gmail.com
Received:
16
May
2019
Accepted:
7
October
2019
Published online:
6
November
2019
We report the results of a global analysis of dark matter simplified models (DMSMs) with leptophobic mediator particles of spin one, considering the cases of both vector and axial-vector interactions with dark matter (DM) particles and quarks. We require the DMSMs to provide all the cosmological DM density indicated by Planck and other observations, and we impose the upper limits on spin-independent and -dependent scattering from direct DM search experiments. We also impose all relevant LHC constraints from searches for monojet events and measurements of the dijet mass spectrum. We model the likelihood functions for all the constraints and combine them within the MasterCode framework, and probe the full DMSM parameter spaces by scanning over the mediator and DM masses and couplings, not fixing any of the model parameters. We find, in general, two allowed regions of the parameter spaces: one in which the mediator couplings to Standard Model (SM) and DM particles may be comparable to those in the SM and the cosmological DM density is reached via resonant annihilation, and one in which the mediator couplings to quarks are 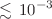 and DM annihilation is non-resonant. We find that the DM and mediator masses may well lie within the ranges accessible to LHC experiments. We also present predictions for spin-independent and -dependent DM scattering, and present specific results for ranges of the DM couplings that may be favoured in ultraviolet completions of the DMSMs.
and DM annihilation is non-resonant. We find that the DM and mediator masses may well lie within the ranges accessible to LHC experiments. We also present predictions for spin-independent and -dependent DM scattering, and present specific results for ranges of the DM couplings that may be favoured in ultraviolet completions of the DMSMs.
© The Author(s), 2019




