https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-019-7344-9
Regular Article - Experimental Physics
Atmospheric charged 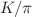 ratio and measurement of muon annual modulation with a liquid scintillation detector at Soudan
ratio and measurement of muon annual modulation with a liquid scintillation detector at Soudan
1
Department of Physics, The University of South Dakota, Vermillion, SD, 57069, USA
2
Natural Sciences Division, Mount Marty College, Yankton, SD, 57078, USA
* e-mail: Dongming.Mei@usd.edu
Received:
22
July
2019
Accepted:
23
September
2019
Published online:
8
October
2019
We report a measurement of muon annual modulation in a 12-l liquid scintillation detector with a live-time of more than 4 years at the Soudan Underground Laboratory. Muon minimum ionization in the detector is identified by its observed pulse shape and large energy deposition. The measured muon rate in the detector is  muons per day with a modulation amplitude of (
muons per day with a modulation amplitude of ( )% and a phase at Jul
)% and a phase at Jul  days. This annual modulation is correlated with the variation of the effective atmospheric temperature in the stratosphere. The correlation coefficient,
days. This annual modulation is correlated with the variation of the effective atmospheric temperature in the stratosphere. The correlation coefficient,  , is determined to be
, is determined to be  . This can be interpreted as a measurement of the atmospheric charged kaon to pion (
. This can be interpreted as a measurement of the atmospheric charged kaon to pion (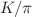 ) ratio of
) ratio of 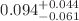 for
for 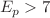 TeV, consistent with the measurement from the MINOS far detector. To further constrain the value of
TeV, consistent with the measurement from the MINOS far detector. To further constrain the value of 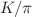 ratio, a Geant4 simulation of the primary cosmic-ray protons with energy up to 100 TeV is implemented to study the correlation of
ratio, a Geant4 simulation of the primary cosmic-ray protons with energy up to 100 TeV is implemented to study the correlation of 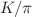 ratio and the muon annual modulation for muon energy greater than 0.5 TeV. We find out that a charged
ratio and the muon annual modulation for muon energy greater than 0.5 TeV. We find out that a charged 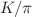 ratio of 0.1598, greater than the upper bound (0.138) from this work at the production point 30 km above the Earth surface in the stratosphere cannot induce muon annual modulation at the depth of Soudan.
ratio of 0.1598, greater than the upper bound (0.138) from this work at the production point 30 km above the Earth surface in the stratosphere cannot induce muon annual modulation at the depth of Soudan.
© The Author(s), 2019




