https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-017-5219-5
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Delocalized SYZ mirrors and confronting top–down SU(3)-structure holographic meson masses at finite g and  with P(article) D(ata) G(roup) values
with P(article) D(ata) G(roup) values
1
Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, Uttarakhand, 247 667, India
2
Physics Department, McGill University, 3600 University St, Montréal, QC, H3A 2T8, Canada
* e-mail: krusldph@iitr.ac.in
Received:
7
August
2017
Accepted:
11
September
2017
Published online:
30
September
2017
Meson spectroscopy at finite gauge coupling – whereat any perturbative QCD computation would break down – and finite number of colors, from a top–down holographic string model, has thus far been entirely missing in the literature. This paper fills this gap. Using the delocalized type IIA SYZ mirror (with SU(3) structure) of the holographic type IIB dual of large-N thermal QCD of Mia et al. (Nucl Phys B 839:187. arXiv:0902.1540 [hep-th], 2010) as constructed in Dhuria and Misra (JHEP 1311:001. arXiv:1306.4339 [hep-th], 2013) at finite coupling and number of colors (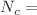 number of
number of 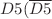 )-branes wrapping a vanishing two-cycle in the top–down holographic construct of Mia et al. (Nucl Phys B 839:187. arXiv:0902.1540 [hep-th], 2010) =
)-branes wrapping a vanishing two-cycle in the top–down holographic construct of Mia et al. (Nucl Phys B 839:187. arXiv:0902.1540 [hep-th], 2010) = 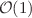 in the IR in the MQGP limit of Dhuria and Misra (JHEP 1311:001. arXiv:1306.4339 [hep-th], 2013) at the end of a Seiberg-duality cascade), we obtain analytical (not just numerical) expressions for the vector and scalar meson spectra and compare our results with previous calculations of Sakai and Sugimoto (Prog Theor Phys 113:843. doi:10.1143/PTP.113.843. arXiv:hep-th/0412141, 2005) and Dasgupta et al. (JHEP 1507:122. doi:10.1007/JHEP07(2015)122. arXiv:1409.0559 [hep-th], 2015), and we obtain a closer match with the Particle Data Group (PDG) results of Olive et al. (Particle Data Group) (Chin Phys C 38:090001, 2014). Through explicit computations, we verify that the vector and scalar meson spectra obtained by the gravity dual with a black hole for all temperatures (small and large) are nearly isospectral with the spectra obtained by a thermal gravity dual valid for only low temperatures; the isospectrality is much closer for vector mesons than scalar mesons. The black-hole gravity dual (with a horizon radius smaller than the deconfinement scale) also provides the expected large-N suppressed decrease in vector meson mass with increase of temperature.
in the IR in the MQGP limit of Dhuria and Misra (JHEP 1311:001. arXiv:1306.4339 [hep-th], 2013) at the end of a Seiberg-duality cascade), we obtain analytical (not just numerical) expressions for the vector and scalar meson spectra and compare our results with previous calculations of Sakai and Sugimoto (Prog Theor Phys 113:843. doi:10.1143/PTP.113.843. arXiv:hep-th/0412141, 2005) and Dasgupta et al. (JHEP 1507:122. doi:10.1007/JHEP07(2015)122. arXiv:1409.0559 [hep-th], 2015), and we obtain a closer match with the Particle Data Group (PDG) results of Olive et al. (Particle Data Group) (Chin Phys C 38:090001, 2014). Through explicit computations, we verify that the vector and scalar meson spectra obtained by the gravity dual with a black hole for all temperatures (small and large) are nearly isospectral with the spectra obtained by a thermal gravity dual valid for only low temperatures; the isospectrality is much closer for vector mesons than scalar mesons. The black-hole gravity dual (with a horizon radius smaller than the deconfinement scale) also provides the expected large-N suppressed decrease in vector meson mass with increase of temperature.
© The Author(s), 2017




