https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-016-4509-7
Review
Review of lattice results concerning low-energy particle physics
Flavour Lattice Averaging Group (FLAG)
1
Center for Gravitational Physics, Yukawa Institute for Theoretical Physics, Kyoto University, Kitashirakawa Oiwakecho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-8502, Japan
2
Kobayashi-Maskawa Institute for the Origin of Particles and the Universe (KMI), Nagoya University, Nagoya, 464-8602, Japan
3
Brookhaven National Laboratory, RIKEN BNL Research Center, Upton, NY, 11973, USA
4
Laboratoire de Physique Théorique (UMR8627), CNRS, Université Paris-Sud, Université Paris-Saclay, 91405, Orsay, France
5
Department of Physics, Washington University, Saint Louis, MO, 63130, USA
6
Physics Department, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269-3046, USA
7
Albert Einstein Center for Fundamental Physics, Institut für Theoretische Physik, Universität Bern, Sidlerstr. 5, 3012, Bern, Switzerland
8
CP3-Origins and Danish IAS, University of Southern Denmark, Campusvej 55, 5230, Odense M, Denmark
9
IFIC (CSIC), c/ Catedrático José Beltrán, 2, 46980, Paterna, Spain
10
Centro Fermi-Museo Storico della Fisica e Centro Studi e Ricerche Enrico Fermi Compendio del Viminale, Piazza del Viminiale 1, 00184, Rome, Italy
11
c/o Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Roma Tor Vergata, Via della Ricerca Scientifica 1, 00133, Rome, Italy
12
University of Wuppertal, Gaußstraße 20, 42119, Wuppertal, Germany
13
Jülich Supercomputing Center, Forschungszentrum Jülich, 52425, Jülich, Germany
14
Department of Physics, Osaka University, Toyonaka, Osaka, 560-0043, Japan
15
Department of Physics and Astronomy, San Francisco State University, San Francisco, CA, 94132, USA
16
Department of Physics, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN, 47405, USA
17
High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK), Tsukuba, 305-0801, Japan
18
School of High Energy Accelerator Science, The Graduate University for Advanced Studies (Sokendai), Tsukuba, 305-0801, Japan
19
American Physical Society (APS), One Research Road, Ridge, NY, 11961, USA
20
Higgs Centre for Theoretical Physics, School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, EH9 3FD, UK
21
School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Southampton, Southampton, SO17 1BJ, UK
22
Centre de Physique Théorique, UMR 7332, CNRS, Aix-Marseille Université, Université de Toulon, 13288, Marseille, France
23
Institute of Physics, National Chiao-Tung University, Hsinchu, 30010, Taiwan
24
Dipartimento di Matematica e Fisica, Università Roma Tre, Via della Vasca Navale 84, 00146, Rome, Italy
25
Sezione di Roma Tre, INFN, Via della Vasca Navale 84, 00146, Rome, Italy
26
Physics Department, Columbia University, New York, NY, 10027, USA
27
Departamento de Física Teórica, Instituto de Física Teórica UAM/CSIC, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Cantoblanco, 28049, Madrid, Spain
28
Physics Department, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, 98195-1560, USA
29
John von Neumann Institute for Computing (NIC), DESY, Platanenallee 6, 15738, Zeuthen, Germany
30
Sezione di Tor Vergata, INFN, c/o Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Roma Tor Vergata, Via della Ricerca Scientifica 1, 00133, Rome, Italy
31
PRISMA Cluster of Excellence, Institut für Kernphysik and Helmholtz Institute Mainz, University of Mainz, 55099, Mainz, Germany
* e-mail: juettner@soton.ac.uk
Received:
6
October
2016
Accepted:
11
November
2016
Published online:
17
February
2017
We review lattice results related to pion, kaon, D- and B-meson physics with the aim of making them easily accessible to the particle-physics community. More specifically, we report on the determination of the light-quark masses, the form factor 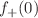 , arising in the semileptonic
, arising in the semileptonic 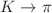 transition at zero momentum transfer, as well as the decay constant ratio
transition at zero momentum transfer, as well as the decay constant ratio 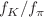 and its consequences for the CKM matrix elements
and its consequences for the CKM matrix elements 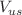 and
and 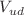 . Furthermore, we describe the results obtained on the lattice for some of the low-energy constants of
. Furthermore, we describe the results obtained on the lattice for some of the low-energy constants of 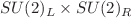 and
and 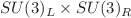 Chiral Perturbation Theory. We review the determination of the
Chiral Perturbation Theory. We review the determination of the 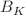 parameter of neutral kaon mixing as well as the additional four B parameters that arise in theories of physics beyond the Standard Model. The latter quantities are an addition compared to the previous review. For the heavy-quark sector, we provide results for
parameter of neutral kaon mixing as well as the additional four B parameters that arise in theories of physics beyond the Standard Model. The latter quantities are an addition compared to the previous review. For the heavy-quark sector, we provide results for 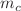 and
and  (also new compared to the previous review), as well as those for D- and B-meson-decay constants, form factors, and mixing parameters. These are the heavy-quark quantities most relevant for the determination of CKM matrix elements and the global CKM unitarity-triangle fit. Finally, we review the status of lattice determinations of the strong coupling constant
(also new compared to the previous review), as well as those for D- and B-meson-decay constants, form factors, and mixing parameters. These are the heavy-quark quantities most relevant for the determination of CKM matrix elements and the global CKM unitarity-triangle fit. Finally, we review the status of lattice determinations of the strong coupling constant 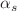 .
.
© The Author(s), 2017




