https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-015-3751-8
Special Article - Tools for Experiment and Theory
Using wavelet analysis to compare the QCD prediction and experimental data on  and to determine parameters of the charmonium states above the
and to determine parameters of the charmonium states above the  threshold
threshold
1
Department of Physics, University of Louisville, Louisville, KY, 40292, USA
2
Department of Theoretical Physics, Perm State University, Perm, 614990, Russia
3
Department of Mathematics, Perm State Technical University, Perm, 614990, Russia
* e-mail: c.l.davis@louisville.edu
Received:
19
June
2015
Accepted:
21
October
2015
Published online:
28
October
2015
The first part of our analysis uses the wavelet method to compare the quantum chromodynamic (QCD) prediction for the ratio of hadronic to muon cross sections in electron-positron collisions, R, with experimental data for R over a center of mass energy range up to about 7 GeV. A direct comparison of the raw experimental data and the QCD prediction is difficult because the data have a wide range of structures and large statistical errors and the QCD description contains sharp quark-antiquark thresholds. However, a meaningful comparison can be made if a type of “smearing” procedure is used to smooth out rapid variations in both the theoretical and experimental values of R. A wavelet analysis (WA) can be used to achieve this smearing effect. The second part of the analysis concentrates on the 3.0–6.0 GeV energy region which includes the relatively wide charmonium resonances 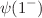 . We use the wavelet methodology to distinguish these resonances from experimental noise, background and from each other, allowing a reliable determination of the parameters of these states. Both analyses are examples of the usefulness of WA in extracting information in a model independent way from high energy physics data.
. We use the wavelet methodology to distinguish these resonances from experimental noise, background and from each other, allowing a reliable determination of the parameters of these states. Both analyses are examples of the usefulness of WA in extracting information in a model independent way from high energy physics data.
© SIF and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2015




