https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-014-3056-3
Regular Article - Experimental Physics
Deep sea tests of a prototype of the KM3NeT digital optical module
KM3NeT Collaboration
1
Instituto de Investigación para la Gestión Integrada de las Zonas Costeras, Universitat Politècnica de València, Gandia, Spain
2
CPPM, Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS/IN2P3, Marseille, France
3
DIAS, Dublin, Ireland
4
INFN, Sezione di Catania, Catania, Italy
5
GRPHE, Université de Haute Alsace, IUT de Colmar, Colmar, France
6
INFN, Sezione di Roma, Rome, Italy
7
Deparment of Physics, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece
8
INFN, Sezione di Genova, Genoa, Italy
9
Erlangen Centre for Astroparticle Physics, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany
10
CEA, Irfu/Sedi, Centre de Saclay, Gif-sur-Yvette, France
11
INFN, Sezione di Napoli, Naples, Italy
12
Institute of Nuclear Physics, NCSR “Demokritos”, Athens, Greece
13
Nikhef, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
14
Dipartimento di Fisica, Università ‘Federico II’, Naples, Italy
15
INFN, Sezione di Bari, Bari, Italy
16
APC,Université Paris Diderot, CNRS/IN2P3, CEA/IRFU Observatoire de Paris, Sorbonne Paris Cité, 75205, Paris, France
17
NESTOR Institute for Deep Sea Research, Technology, and Neutrino Astroparticle Physics, National Observatory of Athens, Pylos, Greece
18
KVI-CART, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands
19
INFN, Sezione di Pisa, Pisa, Italy
20
Dipertimento di Fisica, Università di Pisa, Pisa, Italy
21
INFN, Sezione di Bologna, Bologna, Italy
22
Dipartimento di Fisica e Astronomia, Universitá di Bologna, Bologna, Italy
23
School of Science and Technology, Hellenic Open University, Patras, Greece
24
Leiden Institute of Physics, Leiden University, Leiden, The Netherlands
25
Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Roma La Sapienza, Rome, Italy
26
Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Salerno, Fisciano, Italy
27
Institute of Physics, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
28
INFN, Laboratori Nazionali del Sud, Catania, Italy
29
Université Paris-Sud, 91405, Orsay Cedex, France
30
IFIC-Instituto de Física Corpuscular, (CSIC-Universitat de València), Valencia, Spain
31
Institute of Space Science, Bucharest, Romania
32
Aristotle University Thessaloniki, Thessaloniki, Greece
33
University Würzburg, Würzburg, Germany
34
INFN, Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, Frascati, Italy
35
NIOZ, Texel, The Netherlands
36
Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany
37
Utrecht University, Utrecht, The Netherlands
38
Dr. Remeis Sternwarte, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Bamberg, Germany
39
Dipartimento di Fisica ed Astronomia, Università di Catania, Catania, Italy
40
Physics Department, University of Cyprus, Nicosia, Cyprus
41
University of Aegean, Athens, Greece
42
IPHC, CNRS/IN2P3, Strasbourg, France
43
Oceanlab, University of Aberdeen, Aberdeen, UK
44
Dipartimento di Fisica, Università di Genova, Genoa, Italy
45
CEA, Irfu/SPP, Centre de Saclay, Gif-sur-Yvette, France
46
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK
47
Technological Education Institute of Pireaus, Piraeus, Greece
* e-mail: h84@nikhef.nl
Received:
26
May
2014
Accepted:
22
August
2014
Published online:
26
September
2014
The first prototype of a photo-detection unit of the future KM3NeT neutrino telescope has been deployed in the deep waters of the Mediterranean Sea. This digital optical module has a novel design with a very large photocathode area segmented by the use of 31 three inch photomultiplier tubes. It has been integrated in the ANTARES detector for in-situ testing and validation. This paper reports on the first months of data taking and rate measurements. The analysis results highlight the capabilities of the new module design in terms of background suppression and signal recognition. The directionality of the optical module enables the recognition of multiple Cherenkov photons from the same 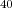 K decay and the localisation of bioluminescent activity in the neighbourhood. The single unit can cleanly identify atmospheric muons and provide sensitivity to the muon arrival directions.
K decay and the localisation of bioluminescent activity in the neighbourhood. The single unit can cleanly identify atmospheric muons and provide sensitivity to the muon arrival directions.
© SIF and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2014




