https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-014-2760-3
Regular Article - Theoretical Physics
Dissipative spherical collapse of charged anisotropic fluid in  gravity
gravity
1
Centre for Applicable Mathematics and Statistics, University of Central Punjab, Lahore, Pakistan
2
University of Management and Technology, Lahore, Pakistan
* e-mail: rizwa_math@yahoo.com
Received:
18
January
2014
Accepted:
27
January
2014
Published online:
25
February
2014
This manuscript is devoted to the study of the combined effect of a viable 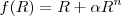 model and the electromagnetic field on the instability range of gravitational collapse. We assume the presence of a charged anisotropic fluid that dissipates energy via heat flow and discuss how the electromagnetic field, density inhomogeneity, shear, and phase transition of astrophysical bodies can be incorporated by a locally anisotropic background. The dynamical equations help to investigate the evolution of self-gravitating objects and lead to the conclusion that the adiabatic index depends upon the electromagnetic background, mass, and radius of the spherical objects.
model and the electromagnetic field on the instability range of gravitational collapse. We assume the presence of a charged anisotropic fluid that dissipates energy via heat flow and discuss how the electromagnetic field, density inhomogeneity, shear, and phase transition of astrophysical bodies can be incorporated by a locally anisotropic background. The dynamical equations help to investigate the evolution of self-gravitating objects and lead to the conclusion that the adiabatic index depends upon the electromagnetic background, mass, and radius of the spherical objects.
© The Author(s), 2014




