https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-012-1947-8
Regular Article - Experimental Physics
Measurement of charged particle multiplicities in pp collisions at  in the forward region
in the forward region
1
CERN, 1211, Geneva 23, Switzerland
2
Centro Brasileiro de Pesquisas Físicas (CBPF), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
3
Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
4
Center for High Energy Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
5
LAPP, Université de Savoie, CNRS/IN2P3, Annecy-Le-Vieux, France
6
LPC, Clermont Université, Université Blaise Pascal, CNRS/IN2P3, Clermont-Ferrand, France
7
CPPM, Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS/IN2P3, Marseille, France
8
LAL, Université Paris-Sud, CNRS/IN2P3, Orsay, France
9
LPNHE, Université Pierre et Marie Curie, Université Paris Diderot, CNRS/IN2P3, Paris, France
10
Fakultät Physik, Technische Universität Dortmund, Dortmund, Germany
11
Max-Planck-Institut für Kernphysik (MPIK), Heidelberg, Germany
12
Physikalisches Institut, Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany
13
School of Physics, University College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
14
Sezione INFN di Bari, Bari, Italy
15
Sezione INFN di Bologna, Bologna, Italy
16
Sezione INFN di Cagliari, Cagliari, Italy
17
Sezione INFN di Ferrara, Ferrara, Italy
18
Sezione INFN di Firenze, Firenze, Italy
19
Laboratori Nazionali dell’INFN di Frascati, Frascati, Italy
20
Sezione INFN di Genova, Genova, Italy
21
Sezione INFN di Milano Bicocca, Milano, Italy
22
Sezione INFN di Roma Tor Vergata, Roma, Italy
23
Sezione INFN di Roma La Sapienza, Roma, Italy
24
Nikhef National Institute for Subatomic Physics, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
25
Nikhef National Institute for Subatomic Physics and Vrije Universiteit, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
26
Henryk Niewodniczanski Institute of Nuclear Physics Polish Academy of Sciences, Kraców, Poland
27
AGH University of Science and Technology, Kraców, Poland
28
Soltan Institute for Nuclear Studies, Warsaw, Poland
29
Horia Hulubei National Institute of Physics and Nuclear Engineering, Bucharest-Magurele, Romania
30
Petersburg Nuclear Physics Institute (PNPI), Gatchina, Russia
31
Institute of Theoretical and Experimental Physics (ITEP), Moscow, Russia
32
Institute of Nuclear Physics, Moscow State University (SINP MSU), Moscow, Russia
33
Institute for Nuclear Research of the Russian Academy of Sciences (INR RAN), Moscow, Russia
34
Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics (SB RAS) and Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk, Russia
35
Institute for High Energy Physics (IHEP), Protvino, Russia
36
Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain
37
Universidad de Santiago de Compostela, Santiago de Compostela, Spain
38
European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN), Geneva, Switzerland
39
Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), Lausanne, Switzerland
40
Physik-Institut, Universität Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland
41
NSC Kharkiv Institute of Physics and Technology (NSC KIPT), Kharkiv, Ukraine
42
Institute for Nuclear Research of the National Academy of Sciences (KINR), Kyiv, Ukraine
43
H.H. Wills Physics Laboratory, University of Bristol, Bristol, United Kingdom
44
Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom
45
Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry, United Kingdom
46
STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Didcot, United Kingdom
47
School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, United Kingdom
48
School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, United Kingdom
49
Oliver Lodge Laboratory, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, United Kingdom
50
Imperial College London, London, United Kingdom
51
School of Physics and Astronomy, University of Manchester, Manchester, United Kingdom
52
Department of Physics, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
53
Syracuse University, Syracuse, NY, United States
54
CC-IN2P3, CNRS/IN2P3, Lyon-Villeurbanne, France
55
Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio de Janeiro (PUC-Rio), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
56
University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom
* e-mail: n.brook@bristol.ac.uk
Received:
4
January
2012
Revised:
8
March
2012
Published online:
20
April
2012
Charged particle production in proton-proton collisions is studied with the LHCb detector at a centre-of-mass energy of 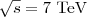 in different intervals of pseudorapidity η. Charged particles are reconstructed close to the interaction region in the vertex detector, which provides high reconstruction efficiency in the η ranges −2.5<η<−2.0 and 2.0<η<4.5. The data were taken with a minimum bias trigger, only requiring one or more reconstructed tracks in the vertex detector. By selecting an event sample with at least one track with a transverse momentum greater than 1 GeV/c a hard QCD subsample is investigated. Several event generators are compared with the data; none are able to describe fully the multiplicity distributions or the charged particle density distribution as a function of η. In general, the models underestimate charged particle production.
in different intervals of pseudorapidity η. Charged particles are reconstructed close to the interaction region in the vertex detector, which provides high reconstruction efficiency in the η ranges −2.5<η<−2.0 and 2.0<η<4.5. The data were taken with a minimum bias trigger, only requiring one or more reconstructed tracks in the vertex detector. By selecting an event sample with at least one track with a transverse momentum greater than 1 GeV/c a hard QCD subsample is investigated. Several event generators are compared with the data; none are able to describe fully the multiplicity distributions or the charged particle density distribution as a function of η. In general, the models underestimate charged particle production.
© Springer-Verlag / Società Italiana di Fisica, 2012




