https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s2006-02613-8
Theoretical Physics
J/ψ gluonic dissociation revisited: III. Effects of transverse hydrodynamic flow
1
Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee, 247 667, India
2
Department of Physics, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, 221 005, India
* e-mail: binoyfph@iitr.ernet.in
Received:
9
January
2006
Revised:
11
May
2006
Published online:
16
August
2006
In a recent paper [B.K. Patra, V.J. Menon, Eur. Phys. J. C 44, 567 (2005)] we developed a very general formulation to take into account explicitly the effects of the hydrodynamic flow profile on the gluonic breakup of J/ψs produced in an equilibrating quark–gluon plasma. Here we apply that formulation to the case when the medium is undergoing a cylindrically symmetric transverse expansion starting from RHIC or LHC initial conditions. Our algebraic and numerical estimates demonstrate that the transverse expansion causes enhancement of the local gluon number density ng, affects the pT-dependence of the average dissociation rate 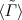 through a partial-wave interference mechanism and makes the survival probability S(pT) to change with pT very slowly. Compared to the previous case of a longitudinal expansion the new graph of S(pT) is pushed up at LHC but develops a rich structure at RHIC, due to a competition between the transverse catch-up time and the plasma lifetime.
through a partial-wave interference mechanism and makes the survival probability S(pT) to change with pT very slowly. Compared to the previous case of a longitudinal expansion the new graph of S(pT) is pushed up at LHC but develops a rich structure at RHIC, due to a competition between the transverse catch-up time and the plasma lifetime.
© Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2006




