https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s2005-02130-4
theoretical physics
The role of strange sea quarks in chiral extrapolations on the lattice
Laboratoire de Physique Théorique, Université Paris-Sud 11, 91405, Orsay Cedex, France
Since the strange quark has a light mass of order  , fluctuations of sea
, fluctuations of sea 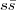 pairs may play a special role in the low-energy dynamics of QCD by inducing significantly different patterns of chiral symmetry breaking in the chiral limits N
f
= 2 (m
u
= m
d
= 0, m
s
physical) and N
f
= 3 (m
u
= m
d
= m
s
= 0). This effect of vacuum fluctuations of
pairs may play a special role in the low-energy dynamics of QCD by inducing significantly different patterns of chiral symmetry breaking in the chiral limits N
f
= 2 (m
u
= m
d
= 0, m
s
physical) and N
f
= 3 (m
u
= m
d
= m
s
= 0). This effect of vacuum fluctuations of 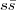 pairs is related to the violation of the Zweig rule in the scalar sector, described through the two O(p
4) low-energy constants L
4 and L
6 of the three-flavour strong chiral lagrangian. In the case of significant vacuum fluctuations, three-flavour chiral expansions might exhibit numerical competition between leading- and next-to-leading-order terms according to the chiral counting, and chiral extrapolations should be handled with special care. We investigate the impact of the fluctuations of
pairs is related to the violation of the Zweig rule in the scalar sector, described through the two O(p
4) low-energy constants L
4 and L
6 of the three-flavour strong chiral lagrangian. In the case of significant vacuum fluctuations, three-flavour chiral expansions might exhibit numerical competition between leading- and next-to-leading-order terms according to the chiral counting, and chiral extrapolations should be handled with special care. We investigate the impact of the fluctuations of 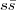 pairs on chiral extrapolations in the case of lattice simulations with three dynamical flavours in the isospin limit. Information on the size of the vacuum fluctuations can be obtained from the dependence of the masses and decay constants of pions and kaons on the light quark masses. Even in the case of large fluctuations, corrections due to the finite size of spatial dimensions can be kept under control for large enough boxes (
pairs on chiral extrapolations in the case of lattice simulations with three dynamical flavours in the isospin limit. Information on the size of the vacuum fluctuations can be obtained from the dependence of the masses and decay constants of pions and kaons on the light quark masses. Even in the case of large fluctuations, corrections due to the finite size of spatial dimensions can be kept under control for large enough boxes ( fm).
fm).
© Springer-Verlag, 2005




