https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s2004-02077-x
experimental physics
Leading-particle suppression in high energy nucleus-nucleus collisions
1
Universitá degli Studi di Padova and INFN, via Marzolo 8, 35131, Padova, Italy
2
Institut für Kernphysik, August-Euler-Str. 6, 60486, Frankfurt am Main, Germany
3
Instituto de Ciencias Nucleares, UNAM, Mexico City, Mexico
* e-mail: andrea.dainese@pd.infn.it
Parton energy loss effects in heavy-ion collisions are studied with the Monte Carlo program PQM (Parton Quenching Model) constructed using the BDMPS quenching weights and a realistic collision geometry. The merit of the approach is that it contains only one free parameter that is tuned to the high-p
t
nuclear modification factor measured in central Au-Au collisions at 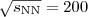 GeV. Once tuned, the model is consistently applied to all the high-p
t
observables at 200 GeV: the centrality evolution of the nuclear modification factor, the suppression of the away-side jet-like correlations, and the azimuthal anisotropies for these observables. Predictions for the leading-particle suppression at nucleon-nucleon centre-of-mass energies of 62.4 and 5500 GeV are presented. The limits of the eikonal approximation in the BDMPS approach, when applied to finite-energy partons, are discussed.
GeV. Once tuned, the model is consistently applied to all the high-p
t
observables at 200 GeV: the centrality evolution of the nuclear modification factor, the suppression of the away-side jet-like correlations, and the azimuthal anisotropies for these observables. Predictions for the leading-particle suppression at nucleon-nucleon centre-of-mass energies of 62.4 and 5500 GeV are presented. The limits of the eikonal approximation in the BDMPS approach, when applied to finite-energy partons, are discussed.
© Springer-Verlag, 2005




