https://doi.org/10.1140/epjc/s10052-025-14352-1
Regular Article - Experimental Physics
CUPID, the Cuore upgrade with particle identification
1
Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA
2
University of California, Los Angeles, CA, USA
3
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, CA, Berkeley, USA
4
CNRS/IN2P3, IP2I-Lyon, Univ Lyon, Université Lyon 1, Villeurbanne, France
5
University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA
6
INFN Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro, Legnaro, Italy
7
National Research Centre Kurchatov Institute, Kurchatov Complex of Theoretical and Experimental Physics, Moscow, Russia
8
INFN Sezione di Bologna, Bologna, Italy
9
Dipartimento di Fisica, Università degli Studi di Milano-Bicocca, Milan, Italy
10
INFN Sezione di Milano-Bicocca, Milan, Italy
11
IRFU, CEA, Université Paris-Saclay, Saclay, France
12
INFN Sezione di Roma, Rome, Italy
13
Sapienza University of Rome, Rome, Italy
14
Gran Sasso Science Institute, L’Aquila, Italy
15
INFN Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso, Assergi (AQ), Italy
16
INFN Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati, Frascati, Italy
17
CNRS/IN2P3, IJCLab, Université Paris-Saclay, Orsay, France
18
CNR-Institute for Microelectronics and Microsystems, Bologna, Italy
19
INFN Sezione di Pavia, Pavia, Italy
20
University of Pavia, Pavia, Italy
21
University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, USA
22
INFN Sezione di Genova, Genoa, Italy
23
University of Genova, Genoa, Italy
24
Fudan University, Shanghai, China
25
Rome Tor Vergata University, Rome, Italy
26
INFN sezione di Roma Tor Vergata, Rome, Italy
27
Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA
28
Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL, USA
29
CNR-Institute of Nanotechnology, Rome, Italy
30
Institute for Nuclear Research of NASU, Kyiv, Ukraine
31
Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA
32
Boston University, Boston, MA, USA
33
California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo, CA, USA
34
Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
35
Yale University, New Haven, CT, USA
36
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
37
Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, USA
38
Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
39
Beijing Normal University, Beijing, China
40
Centro de Astropartículas y Física de Altas Energías, Universidad de Zaragoza, Zaragoza, Spain
41
University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China
42
Nikolaev Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, Novosibirsk, Russia
43
INFN Sezione di Padova, Padua, Italy
44
Univ. Grenoble Alpes, CNRS, Grenoble INP, SIMAP, Grenoble, France
45
University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy
46
IP2I-Lyon, Univ Lyon, France
47
Physik-Institut, University of Zürich, Zurich, Switzerland
48
University College London, London, UK
49
Instituto de Física, Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil
50
Brazil and Max-Planck-Institut für Physik, Munich, Germany
51
Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso, Assergi, Italy
a
cupid.publications@lngs.infn.it
Received:
5
March
2025
Accepted:
22
May
2025
Published online:
3
July
2025
CUPID, the CUORE Upgrade with Particle Identification, is a next-generation experiment to search for neutrinoless double beta decay (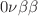 ) and other rare events using enriched Li
) and other rare events using enriched Li
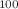 MoO
MoO scintillating bolometers. It will be hosted by the CUORE cryostat located at the Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso in Italy. The main physics goal of CUPID is to search for
scintillating bolometers. It will be hosted by the CUORE cryostat located at the Laboratori Nazionali del Gran Sasso in Italy. The main physics goal of CUPID is to search for 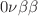 of
of 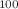 Mo with a discovery sensitivity covering the full neutrino mass regime in the inverted ordering scenario, as well as the portion of the normal ordering regime with lightest neutrino mass larger than 10 meV. With a conservative background index of 10
Mo with a discovery sensitivity covering the full neutrino mass regime in the inverted ordering scenario, as well as the portion of the normal ordering regime with lightest neutrino mass larger than 10 meV. With a conservative background index of 10 cts
cts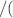 keV
keV kg
kg yr
yr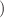 , 240 kg isotope mass, 5 keV FWHM energy resolution at 3 MeV and 10 live-years of data taking, CUPID will have a 90% C.L. half-life exclusion sensitivity of
, 240 kg isotope mass, 5 keV FWHM energy resolution at 3 MeV and 10 live-years of data taking, CUPID will have a 90% C.L. half-life exclusion sensitivity of 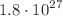 yr, corresponding to an effective Majorana neutrino mass (
yr, corresponding to an effective Majorana neutrino mass (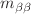 ) sensitivity of 9–15 meV, and a
) sensitivity of 9–15 meV, and a 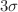 discovery sensitivity of
discovery sensitivity of 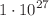 yr, corresponding to an
yr, corresponding to an 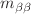 range of 12–21 meV.
range of 12–21 meV.
© The Author(s) 2025
 Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
Funded by SCOAP3.




